 React 首次渲染过程
React 首次渲染过程
# 目录
注意
- 本文的代码去除了 dev 环境的部分代码。
# ReactDOM.render
通过在 ReactDOM.render 语句添加断点,我们来追溯一下 React 的首次渲染过程。
# jsxWithValidation
首先开始验证 <App /> 组件是否是合法的 jsx 组件。如果不合法,就打印错误消息和错误栈信息。
// src/react/fixtures/legacy-jsx-runtimes/react-17/cjs/react-jsx-dev-runtime.development.js
function jsxWithValidation(type, props, key, isStaticChildren, source, self) {
{
var validType = isValidElementType(type); // We warn in this case but don't throw. We expect the element creation to
// succeed and there will likely be errors in render.
if (!validType) {
// pass
// 报错处理
}
// 返回一个 ReactElement 对象
var element = jsxDEV(type, props, key, source, self); // The result can be nullish if a mock or a custom function is used.
// TODO: Drop this when these are no longer allowed as the type argument.
if (element == null) {
return element;
} // Skip key warning if the type isn't valid since our key validation logic
// doesn't expect a non-string/function type and can throw confusing errors.
// We don't want exception behavior to differ between dev and prod.
// (Rendering will throw with a helpful message and as soon as the type is
// fixed, the key warnings will appear.)
if (validType) {
var children = props.children;
if (children !== undefined) {
// isStaticChildren 则校验 key 值
if (isStaticChildren) {
if (Array.isArray(children)) {
for (var i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
validateChildKeys(children[i], type);
}
if (Object.freeze) {
Object.freeze(children);
}
} else {
error('React.jsx: Static children should always be an array. ' + 'You are likely explicitly calling React.jsxs or React.jsxDEV. ' + 'Use the Babel transform instead.');
}
} else {
validateChildKeys(children, type);
}
}
}
if (type === exports.Fragment) {
validateFragmentProps(element);
} else {
validatePropTypes(element);
}
return element;
}
}
// Local Stack
// {
// "props": {},
// "isStaticChildren": false,
// "source": {
// "fileName": "/Users/jonsam/Projects/update_in_github/react-source-reading/src/index.js",
// "lineNumber": 9,
// "columnNumber": 5
// },
// "validType": true,
// "element": {
// "key": null,
// "ref": null,
// "props": {},
// "_owner": null,
// "_store": {}
// }
// }
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
那么如何判断是否是合法的 Element 呢?
function isValidElementType(type) {
// 如果是 string 和 function 是合法的 Element,分别代表着文本节点和 FC
if (typeof type === 'string' || typeof type === 'function') {
return true;
} // Note: typeof might be other than 'symbol' or 'number' (e.g. if it's a polyfill).
// 判断 type 是否为 Fragment,profiler,suspense 之类的特殊类型
if (type === exports.Fragment || type === REACT_PROFILER_TYPE || type === REACT_DEBUG_TRACING_MODE_TYPE || type === REACT_STRICT_MODE_TYPE || type === REACT_SUSPENSE_TYPE || type === REACT_SUSPENSE_LIST_TYPE || type === REACT_LEGACY_HIDDEN_TYPE || enableScopeAPI ) {
return true;
}
// 判断 $$typeof 书否为内部类型,LAZY、MEMO、PROVIDER、CONTEXT、FORWARD_REF 等
if (typeof type === 'object' && type !== null) {
if (type.$$typeof === REACT_LAZY_TYPE || type.$$typeof === REACT_MEMO_TYPE || type.$$typeof === REACT_PROVIDER_TYPE || type.$$typeof === REACT_CONTEXT_TYPE || type.$$typeof === REACT_FORWARD_REF_TYPE || type.$$typeof === REACT_FUNDAMENTAL_TYPE || type.$$typeof === REACT_BLOCK_TYPE || type[0] === REACT_SERVER_BLOCK_TYPE) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
jsxDEV 如何返回一个 ReactElement 呢?
var ReactElement = function (type, key, ref, self, source, owner, props) {
var element = {
// This tag allows us to uniquely identify this as a React Element
// 添加 ReactElement 的 $$typeof 类型
$$typeof: REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE,
// Built-in properties that belong on the element
// 节点实际的类型,此处为 function
type: type,
key: key,
ref: ref,
props: props,
// Record the component responsible for creating this element.
_owner: owner
};
{
// The validation flag is currently mutative. We put it on
// an external backing store so that we can freeze the whole object.
// This can be replaced with a WeakMap once they are implemented in
// commonly used development environments.
// 使用外部的代码块防止变量因为 _store 的引用而不能释放,可以放 weakMap 代替,给 element 添加类似于 weakMap 的 _store 属性
element._store = {}; // To make comparing ReactElements easier for testing purposes, we make
// the validation flag non-enumerable (where possible, which should
// include every environment we run tests in), so the test framework
// ignores it.
Object.defineProperty(element._store, 'validated', {
configurable: false,
enumerable: false,
writable: true,
value: false
}); // self and source are DEV only properties.
Object.defineProperty(element, '_self', {
configurable: false,
enumerable: false,
writable: false,
value: self
}); // Two elements created in two different places should be considered
// equal for testing purposes and therefore we hide it from enumeration.
Object.defineProperty(element, '_source', {
configurable: false,
enumerable: false,
writable: false,
value: source
});
if (Object.freeze) {
Object.freeze(element.props);
Object.freeze(element);
}
}
return element;
};
// Local Stack
// {
// "config": {},
// "source": {
// "fileName": "/Users/jonsam/Projects/update_in_github/react-source-reading/src/index.js",
// "lineNumber": 9,
// "columnNumber": 5
// },
// "props": {},
// "key": null,
// "ref": null
// }
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
- ReactElement 是一个工厂函数,传入相关的属性,生成 ReactElement 对象。
- ReactElement 中
$$typeof是指内部的节点类型,ReactElement 的内部类型为REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE,type 是指实际的节点类型,此处是一个 function。 - 在测试环境下会在 ReactElement 上挂载 _store 属性,类似于 weakMap 是为了节省内存,目的是为了开发环境中测试提速。
# render
// src/react/packages/react-dom/src/client/ReactDOMLegacy.js
function render(
element: React$Element<any>,
container: Container,
callback: ?Function,
){
if (!isValidContainerLegacy(container)) {
throw new Error('Target container is not a DOM element.');
}
return legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer(
null,
element,
container,
false,
callback,
);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
Local Stack
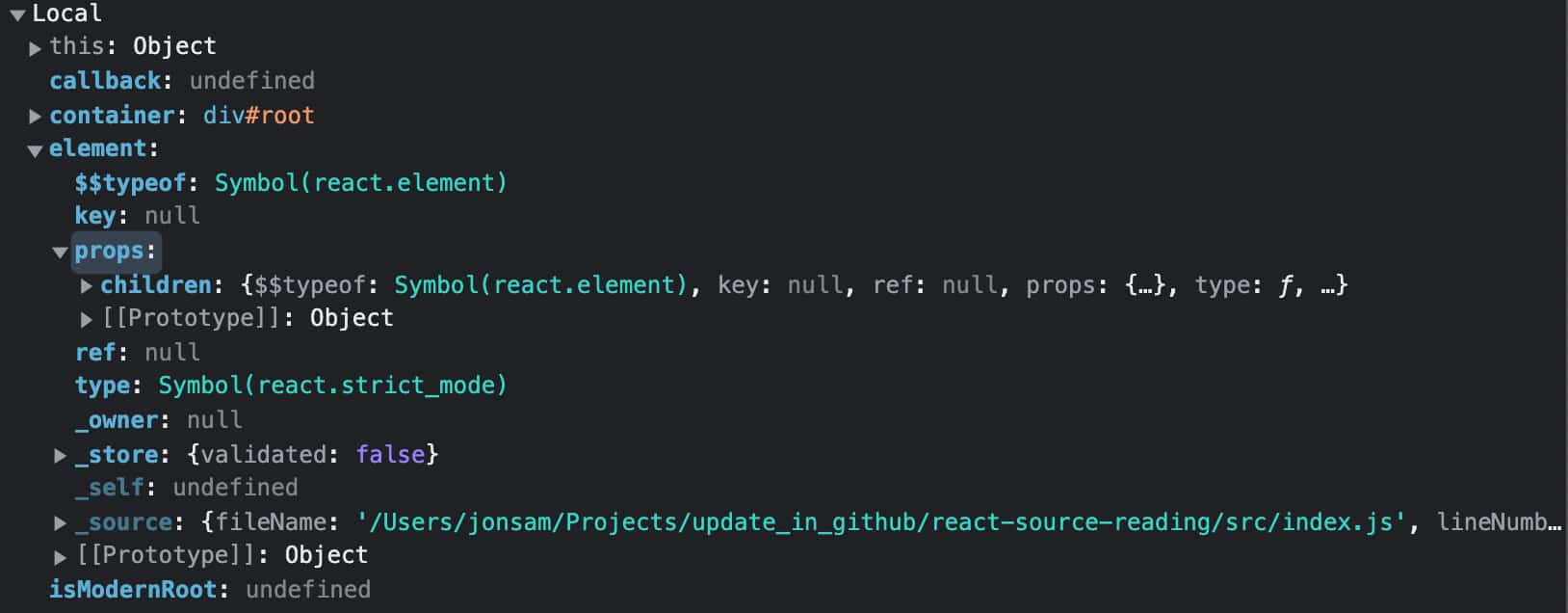
生成 ReactElement 之后调用 render 方法,内部判断是否是合法的 container,然后调用 legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer 方法将 subTree 渲染到 container 中。
怎么判断是否是合法的 container 呢?
// We only use it in places that are currently more relaxed.
export function isValidContainerLegacy(node: any): boolean {
// 通过 node.nodeType 来判断 node 是否是已知的类型
return !!(
node &&
(node.nodeType === ELEMENT_NODE ||
node.nodeType === DOCUMENT_NODE ||
node.nodeType === DOCUMENT_FRAGMENT_NODE ||
(node.nodeType === COMMENT_NODE &&
(node: any).nodeValue === ' react-mount-point-unstable '))
);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Local Stack
去除可访问性和事件之后的属性:
assignedSlot: null
attributeStyleMap: StylePropertyMap {size: 0}
attributes: NamedNodeMap {0: id, id: id, length: 1}
autocapitalize: ""
autofocus: false
baseURI: "http://localhost:3001/"
childElementCount: 0
childNodes: NodeList []
children: HTMLCollection []
classList: DOMTokenList [value: '']
className: ""
clientHeight: 0
clientLeft: 0
clientTop: 0
clientWidth: 1792
contentEditable: "inherit"
dataset: DOMStringMap {}
dir: ""
draggable: false
elementTiming: ""
enterKeyHint: ""
firstChild: null
firstElementChild: null
hidden: false
id: "root"
innerHTML: ""
innerText: ""
inputMode: ""
isConnected: true
isContentEditable: false
lang: ""
lastChild: null
lastElementChild: null
localName: "div"
namespaceURI: "http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
nextElementSibling: null
nextSibling: text
nodeName: "DIV"
nodeType: 1
nodeValue: null
nonce: ""
offsetHeight: 0
offsetLeft: 0
offsetParent: body
offsetTop: 0
offsetWidth: 1792
outerHTML: "<div id=\"root\"></div>"
outerText: ""
ownerDocument: document
parentElement: body
parentNode: body
part: DOMTokenList [value: '']
prefix: null
previousElementSibling: noscript
previousSibling: text
scrollHeight: 0
scrollLeft: 0
scrollTop: 0
scrollWidth: 1792
shadowRoot: null
slot: ""
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
可以看到,这里 nodeType: 1,即为 ELEMENT_NODE。
# legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer
// src/react/packages/react-dom/src/client/ReactDOMLegacy.js
function legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer(
parentComponent: ?React$Component<any, any>,
children: ReactNodeList,
container: Container,
forceHydrate: boolean,
callback: ?Function,
) {
// 判断是否已经创建过 RootContainer
// _reactRootContainer 标记为 container 上的 FiberRoot 对象
let root = container._reactRootContainer;
let fiberRoot: FiberRoot;
if (!root) {
// Initial mount
// RootContainer 未创建则为首次挂载应用,调用 legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer 创建 Root
root = container._reactRootContainer = legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer(
container,
forceHydrate,
);
fiberRoot = root;
// 如果在 render 函数中传入了 callback,需要调用 callback
if (typeof callback === 'function') {
const originalCallback = callback;
callback = function() {
const instance = getPublicRootInstance(fiberRoot);
originalCallback.call(instance);
};
}
// Initial mount should not be batched.
// 在 mount 阶段,以最高优先级同步的执行所有的更新
flushSync(() => {
updateContainer(children, fiberRoot, parentComponent, callback);
});
} else {
fiberRoot = root;
if (typeof callback === 'function') {
const originalCallback = callback;
callback = function() {
const instance = getPublicRootInstance(fiberRoot);
originalCallback.call(instance);
};
}
// Update
updateContainer(children, fiberRoot, parentComponent, callback);
}
return getPublicRootInstance(fiberRoot);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
Local Stack
当前传入的变量:
callback: undefined
children: {$$typeof: Symbol(react.element), type: Symbol(react.strict_mode), key: null, ref: null, props: {…}, …}
container: div#root
fiberRoot: undefined
forceHydrate: false
originalCallback: undefined
parentComponent: null
root: undefined
_originalCallback: undefined
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
render 函数中 callback 返回当前容器(container)中的 FiberRoot 对象,由下面这个递归的函数可见:
export function getPublicRootInstance(
container: OpaqueRoot,
): React$Component<any, any> | PublicInstance | null {
const containerFiber = container.current;
if (!containerFiber.child) {
return null;
}
switch (containerFiber.child.tag) {
case HostComponent:
return getPublicInstance(containerFiber.child.stateNode);
default:
// 最终返回的有效的 instance 是 Fiber.child.stateNode 刚好是 RootFiber
return containerFiber.child.stateNode;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer
RootContainer 是如何根据 container 创建的呢?我们来追溯下 legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer 函数:
function legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer(
container: Container,
forceHydrate: boolean,
): FiberRoot {
// First clear any existing content.
// 如果不是 SSR,就清空 container 中所有的节点
if (!forceHydrate) {
let rootSibling;
while ((rootSibling = container.lastChild)) {
container.removeChild(rootSibling);
}
}
// 调用 createContainer 创建 RootContainer
const root = createContainer(
container,
// export const LegacyRoot = 0;
// export const ConcurrentRoot = 1;
LegacyRoot,
forceHydrate,
null, // hydrationCallbacks
false, // isStrictMode
false, // concurrentUpdatesByDefaultOverride,
'', // identifierPrefix
);
// 将 FiberRoot 挂载到 container 上,便于下次使用
markContainerAsRoot(root.current, container);
const rootContainerElement =
container.nodeType === COMMENT_NODE ? container.parentNode : container;
// 开启 container 上所支持的事件监听
listenToAllSupportedEvents(rootContainerElement);
return root;
}
// src/react/packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberReconciler.new.js
export function createContainer(
containerInfo: Container,
tag: RootTag,
hydrate: boolean,
hydrationCallbacks: null | SuspenseHydrationCallbacks,
isStrictMode: boolean,
concurrentUpdatesByDefaultOverride: null | boolean,
identifierPrefix: string,
): OpaqueRoot {
return createFiberRoot(
containerInfo,
tag,
hydrate,
hydrationCallbacks,
isStrictMode,
concurrentUpdatesByDefaultOverride,
identifierPrefix,
);
}
// src/react/packages/react-dom/src/client/ReactDOMComponentTree.js
export function markContainerAsRoot(hostRoot: Fiber, node: Container): void {
// 将 FiberRoot 挂载到相应的 container 上
// internalContainerInstanceKey: "__reactFiber$9yvlviys3ft"
node[internalContainerInstanceKey] = hostRoot;
}
// randomKey 是每次启动应用生成的随机的 key 值,被应用在内部一些 key 值的使用上
const randomKey = Math.random()
.toString(36)
.slice(2);
const internalContainerInstanceKey = '__reactContainer$' + randomKey;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
- RootContainer 分为了两种:LegacyRoot 和 ConcurrentRoot。分别代表着这 React 运行的两种模式:Legacy Mode 和 Concurrent Mode。
- RootContainer 实际上就是 FiberRoot。这里开始了从 ReactElement 到 FiberRoot 的创建过程。注意 FiberRoot(HostRoot) 本质上是 Root,不是 Fiber;而 RootFiber 才是 Fiber,才是 FiberTree 的根。
- randomKey 之所以要随机生成,有以下两点原因:标记是打在 node 这样的原生节点上的,随机的标记名可以防止将用户或者其他库所生成的标记覆盖,同时加上
__reactContainer$这样的特征串更能防止重复;随机的标记更加安全,防止被其他程序更改或者恶意篡改造成程序崩溃。
# listenToAllSupportedEvents
container 上的事件是如何委托监听的呢,我们来看下 listenToAllSupportedEvents 这个函数:
// src/react/packages/react-dom/src/events/DOMPluginEventSystem.js
// 为当前的应用生成随机的监听器标记
const listeningMarker =
'_reactListening' +
Math.random()
.toString(36)
.slice(2);
// We should not delegate these events to the container, but rather
// set them on the actual target element itself. This is primarily
// because these events do not consistently bubble in the DOM.
// 如下事件不能委托在 container 上,需要设置在实际的 target element 上,这是因为他们不能持续的冒泡。
// 不能持续冒泡的事件的集合
export const nonDelegatedEvents: Set<DOMEventName> = new Set([
'cancel',
'close',
'invalid',
'load',
'scroll',
'toggle',
// In order to reduce bytes, we insert the above array of media events
// into this Set. Note: the "error" event isn't an exclusive media event,
// and can occur on other elements too. Rather than duplicate that event,
// we just take it from the media events array.
// 将媒体先关的事件加入这里以节省内存。
...mediaEventTypes,
]);
// List of events that need to be individually attached to media elements.
export const mediaEventTypes: Array<DOMEventName> = [
'abort',
'canplay',
'canplaythrough',
'durationchange',
'emptied',
'encrypted',
'ended',
'error',
'loadeddata',
'loadedmetadata',
'loadstart',
'pause',
'play',
'playing',
'progress',
'ratechange',
'resize',
'seeked',
'seeking',
'stalled',
'suspend',
'timeupdate',
'volumechange',
'waiting',
];
export function listenToAllSupportedEvents(rootContainerElement: EventTarget) {
if (!(rootContainerElement: any)[listeningMarker]) {
// 将事件监听标记设为 true,防止重复监听
(rootContainerElement: any)[listeningMarker] = true;
allNativeEvents.forEach(domEventName => {
// We handle selectionchange separately because it
// doesn't bubble and needs to be on the document.
// 除 selectionchange 事件之外,其余事件如果可以持续的冒泡,就开启原生事件监听,从冒泡阶段监听;如果无法持续冒泡,从捕获阶段监听。
// selectionchange 将会单独处理,因为此事件不允许冒泡,而且必须在 document 上监听
if (domEventName !== 'selectionchange') {
if (!nonDelegatedEvents.has(domEventName)) {
listenToNativeEvent(domEventName, false, rootContainerElement);
}
listenToNativeEvent(domEventName, true, rootContainerElement);
}
});
// 获取 container 所在的 document
const ownerDocument =
(rootContainerElement: any).nodeType === DOCUMENT_NODE
? rootContainerElement
: (rootContainerElement: any).ownerDocument;
if (ownerDocument !== null) {
// The selectionchange event also needs deduplication
// but it is attached to the document.
if (!(ownerDocument: any)[listeningMarker]) {
// 在 container 所在的 document 上单独监听 selectionchange 事件
(ownerDocument: any)[listeningMarker] = true;
listenToNativeEvent('selectionchange', false, ownerDocument);
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
先总结一下如上的代码:
- react 中为提高应用的性能,采用了事件委托机制来来统一处理事件。事件被委托到 container 上或者是 document 上。
- react 将事件分为三类,一类是可以在冒泡过程中监听的,一类是可以在冒泡过程中监听需要在捕获中监听的,还有一类是在 document 上监听的,如 selectionchange。
- react 将所有的原生事件都委托了一遍,原因在于基于 react 子树的时间监听将统一由受委托的容器来进行监听。
以上是 react 事件监听的策略,真正的时间监听在函数 listenToNativeEvent 实现。那么 listenToNativeEvent 是如何监听原生事件的呢?请参见 React 中的事件监听机制
# createFiberRoot
export function createFiberRoot(
containerInfo: any,
tag: RootTag,
hydrate: boolean,
hydrationCallbacks: null | SuspenseHydrationCallbacks,
isStrictMode: boolean,
concurrentUpdatesByDefaultOverride: null | boolean,
identifierPrefix: string,
): FiberRoot {
// 根据 containerInfo 等信息创建 FiberRoot 对象
const root: FiberRoot = (new FiberRootNode(
containerInfo,
tag,
hydrate,
identifierPrefix,
): any);
if (enableSuspenseCallback) {
root.hydrationCallbacks = hydrationCallbacks;
}
// Cyclic construction. This cheats the type system right now because
// stateNode is any.
// 创建与 HostRoot 强关联的 RootFiber
const uninitializedFiber = createHostRootFiber(
tag,
isStrictMode,
concurrentUpdatesByDefaultOverride,
);
// HostRoot 与 RootFiber 双向链接 HostRoot.current = RootFiber; RootFiber.stateNode = HostRoot
root.current = uninitializedFiber;
uninitializedFiber.stateNode = root;
// 初始化 RootFiber 上的更新队列
initializeUpdateQueue(uninitializedFiber);
return root;
}
function FiberRootNode(containerInfo, tag, hydrate, identifierPrefix) {
this.tag = tag;
this.containerInfo = containerInfo;
this.pendingChildren = null;
this.current = null;
this.pingCache = null;
this.finishedWork = null;
this.timeoutHandle = noTimeout;
this.context = null;
this.pendingContext = null;
this.isDehydrated = hydrate;
this.callbackNode = null;
this.callbackPriority = NoLane;
this.eventTimes = createLaneMap(NoLanes);
this.expirationTimes = createLaneMap(NoTimestamp);
this.pendingLanes = NoLanes;
this.suspendedLanes = NoLanes;
this.pingedLanes = NoLanes;
this.expiredLanes = NoLanes;
this.mutableReadLanes = NoLanes;
this.finishedLanes = NoLanes;
this.entangledLanes = NoLanes;
this.entanglements = createLaneMap(NoLanes);
this.identifierPrefix = identifierPrefix;
if (enableCache) {
this.pooledCache = null;
this.pooledCacheLanes = NoLanes;
}
if (supportsHydration) {
this.mutableSourceEagerHydrationData = null;
}
if (enableSuspenseCallback) {
this.hydrationCallbacks = null;
}
if (enableProfilerTimer && enableProfilerCommitHooks) {
this.effectDuration = 0;
this.passiveEffectDuration = 0;
}
if (enableUpdaterTracking) {
this.memoizedUpdaters = new Set();
const pendingUpdatersLaneMap = (this.pendingUpdatersLaneMap = []);
for (let i = 0; i < TotalLanes; i++) {
pendingUpdatersLaneMap.push(new Set());
}
}
}
// 在 fiber 上初始化一个更新队列
export function initializeUpdateQueue<State>(fiber: Fiber): void {
const queue: UpdateQueue<State> = {
baseState: fiber.memoizedState,
firstBaseUpdate: null,
lastBaseUpdate: null,
shared: {
pending: null,
interleaved: null,
lanes: NoLanes,
},
effects: null,
};
fiber.updateQueue = queue;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
Local Stack
createFiberRoot 函数的变量栈:
containerInfo: div#root
hydrate: false
hydrationCallbacks: undefined
root: FiberRootNode
callbackNode: null
callbackPriority: 0
containerInfo: div#root
context: null
current: FiberNode
actualDuration: 0
actualStartTime: -1
alternate: null
child: null
childLanes: 0
dependencies: null
elementType: null
firstEffect: null
flags: 0
index: 0
key: null
lanes: 0
lastEffect: null
memoizedProps: null
memoizedState: null
mode: 8
nextEffect: null
pendingProps: null
ref: null
return: null
selfBaseDuration: 0
sibling: null
stateNode: FiberRootNode {tag: 0, containerInfo: div#root, pendingChildren: null, current: FiberNode, pingCache: null, …}
tag: 3
treeBaseDuration: 0
type: null
updateQueue:
baseState: null
effects: null
firstBaseUpdate: null
lastBaseUpdate: null
shared: {pending: null}
[[Prototype]]: Object
_debugHookTypes: null
_debugID: 1
_debugNeedsRemount: false
_debugOwner: null
_debugSource: null
[[Prototype]]: Object
entangledLanes: 0
entanglements: (31) [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
eventTimes: (31) [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
expirationTimes: (31) [-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1]
expiredLanes: 0
finishedLanes: 0
finishedWork: null
hydrate: false
interactionThreadID: 1
memoizedInteractions: Set(0) {size: 0}
mutableReadLanes: 0
mutableSourceEagerHydrationData: null
pendingChildren: null
pendingContext: null
pendingInteractionMap: Map(0) {size: 0}
pendingLanes: 0
pingCache: null
pingedLanes: 0
suspendedLanes: 0
tag: 0
timeoutHandle: -1
_debugRootType: "createLegacyRoot()"
[[Prototype]]: Object
tag: 0
uninitializedFiber: FiberNode {tag: 3, key: null, elementType: null, type: null, stateNode: FiberRootNode, …}
Closure
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
# createHostRootFiber
export function createHostRootFiber(
tag: RootTag,
isStrictMode: boolean,
concurrentUpdatesByDefaultOverride: null | boolean,
): Fiber {
let mode;
if (tag === ConcurrentRoot) {
mode = ConcurrentMode;
if (isStrictMode === true) {
mode |= StrictLegacyMode;
if (enableStrictEffects) {
mode |= StrictEffectsMode;
}
} else if (enableStrictEffects && createRootStrictEffectsByDefault) {
mode |= StrictLegacyMode | StrictEffectsMode;
}
if (
// We only use this flag for our repo tests to check both behaviors.
// TODO: Flip this flag and rename it something like "forceConcurrentByDefaultForTesting"
!enableSyncDefaultUpdates ||
// Only for internal experiments.
(allowConcurrentByDefault && concurrentUpdatesByDefaultOverride)
) {
mode |= ConcurrentUpdatesByDefaultMode;
}
} else {
mode = NoMode;
}
if (enableProfilerTimer && isDevToolsPresent) {
// Always collect profile timings when DevTools are present.
// This enables DevTools to start capturing timing at any point–
// Without some nodes in the tree having empty base times.
mode |= ProfileMode;
}
return createFiber(HostRoot, null, null, mode);
}
// This is a constructor function, rather than a POJO constructor, still
// please ensure we do the following:
// 1) Nobody should add any instance methods on this. Instance methods can be
// more difficult to predict when they get optimized and they are almost
// never inlined properly in static compilers.
// 2) Nobody should rely on `instanceof Fiber` for type testing. We should
// always know when it is a fiber.
// 3) We might want to experiment with using numeric keys since they are easier
// to optimize in a non-JIT environment.
// 4) We can easily go from a constructor to a createFiber object literal if that
// is faster.
// 5) It should be easy to port this to a C struct and keep a C implementation
// compatible.
// createFiber 是一个工厂函数,不支持构造器、instanceof 语法
const createFiber = function(
tag: WorkTag,
pendingProps: mixed,
key: null | string,
mode: TypeOfMode,
): Fiber {
// $FlowFixMe: the shapes are exact here but Flow doesn't like constructors
return new FiberNode(tag, pendingProps, key, mode);
};
function FiberNode(
tag: WorkTag,
pendingProps: mixed,
key: null | string,
mode: TypeOfMode,
) {
// Instance
this.tag = tag;
this.key = key;
this.elementType = null;
this.type = null;
this.stateNode = null;
// Fiber
this.return = null;
this.child = null;
this.sibling = null;
this.index = 0;
this.ref = null;
this.pendingProps = pendingProps;
this.memoizedProps = null;
this.updateQueue = null;
this.memoizedState = null;
this.dependencies = null;
this.mode = mode;
// Effects
this.flags = NoFlags;
this.subtreeFlags = NoFlags;
this.deletions = null;
this.lanes = NoLanes;
this.childLanes = NoLanes;
this.alternate = null;
if (enableProfilerTimer) {
// Note: The following is done to avoid a v8 performance cliff.
//
// Initializing the fields below to smis and later updating them with
// double values will cause Fibers to end up having separate shapes.
// This behavior/bug has something to do with Object.preventExtension().
// Fortunately this only impacts DEV builds.
// Unfortunately it makes React unusably slow for some applications.
// To work around this, initialize the fields below with doubles.
//
// Learn more about this here:
// https://github.com/facebook/react/issues/14365
// https://bugs.chromium.org/p/v8/issues/detail?id=8538
this.actualDuration = Number.NaN;
this.actualStartTime = Number.NaN;
this.selfBaseDuration = Number.NaN;
this.treeBaseDuration = Number.NaN;
// It's okay to replace the initial doubles with smis after initialization.
// This won't trigger the performance cliff mentioned above,
// and it simplifies other profiler code (including DevTools).
this.actualDuration = 0;
this.actualStartTime = -1;
this.selfBaseDuration = 0;
this.treeBaseDuration = 0;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
- RootFiber 本质上是 Fiber 的原因是调用了 createFiber 来构造 Fiber,同时传入的 tag 为 HostRoot 保证了 Fiber 的独特性。
- Fiber 的本质是一个对象。Fiber 上的重要属性大致分为三类:Instance 相关、Fiber 相关、Effects 相关、lanes 相关。instance 相关为 Fiber 对象实例的属性,tag 为 fiber 上节点类型标记。Fiber 相关为 FiberTree 的必要指针;Effects 相关为 render 过程中副作用的标记。lanes 为优先级相关的属性,alternate 则是版本记录的属性。
- uninitializedFiber 不是完整的 RootFiber,其中只初始化了 Instance 相关 的属性。
注意
- tag 不是 Fiber 的类型,而是 Fiber 上标记的节点的类型。
Local Stack
Return value: FiberNode
actualDuration: 0
actualStartTime: -1
alternate: null
child: null
childLanes: 0
dependencies: null
elementType: null
firstEffect: null
flags: 0
index: 0
key: null
lanes: 0
lastEffect: null
memoizedProps: null
memoizedState: null
mode: 8
nextEffect: null
pendingProps: null
ref: null
return: null
selfBaseDuration: 0
sibling: null
stateNode: null
tag: 3
treeBaseDuration: 0
type: null
updateQueue: null
_debugHookTypes: null
_debugID: 1
_debugNeedsRemount: false
_debugOwner: null
_debugSource: null
[[Prototype]]: Object
this: undefined
mode: 8
tag: 0
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
WorkTag 是怎么分类的,Fiber 标记了哪些类型?
// src/react/packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactWorkTags.js
export type WorkTag =
| 0
| 1
| 2
| 3
| 4
| 5
| 6
| 7
| 8
| 9
| 10
| 11
| 12
| 13
| 14
| 15
| 16
| 17
| 18
| 19
| 20
| 21
| 22
| 23
| 24;
export const FunctionComponent = 0; // 函数组件
export const ClassComponent = 1; // 类组件
export const IndeterminateComponent = 2; // Before we know whether it is function or class // 未知类型组件,在未知为函数组件还是类组件时使用
export const HostRoot = 3; // Root of a host tree. Could be nested inside another node. // HostRoot 是包含 RootFiber 信息的容器
export const HostPortal = 4; // A subtree. Could be an entry point to a different renderer. // HostPortal 是类型为 Portal 的 HostRoot
export const HostComponent = 5;
export const HostText = 6;
export const Fragment = 7; // React.Fragment 类型
export const Mode = 8;
export const ContextConsumer = 9; // context.Consumer 类型
export const ContextProvider = 10; // context.Provider 类型
export const ForwardRef = 11; // React.forwardRef 类型
export const Profiler = 12;
export const SuspenseComponent = 13; // suspense 组件类型
export const MemoComponent = 14; // memo 组件类型
export const SimpleMemoComponent = 15; // 没有 compare 的简单的 memo 组件类型
export const LazyComponent = 16; // react.lazy 的组件类型
export const IncompleteClassComponent = 17;
export const DehydratedFragment = 18;
export const SuspenseListComponent = 19;
export const ScopeComponent = 21;
export const OffscreenComponent = 22;
export const LegacyHiddenComponent = 23;
export const CacheComponent = 24;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
FiberNode 中 Fiber 相关的属性构成了怎样的 FiberTree 的关系?
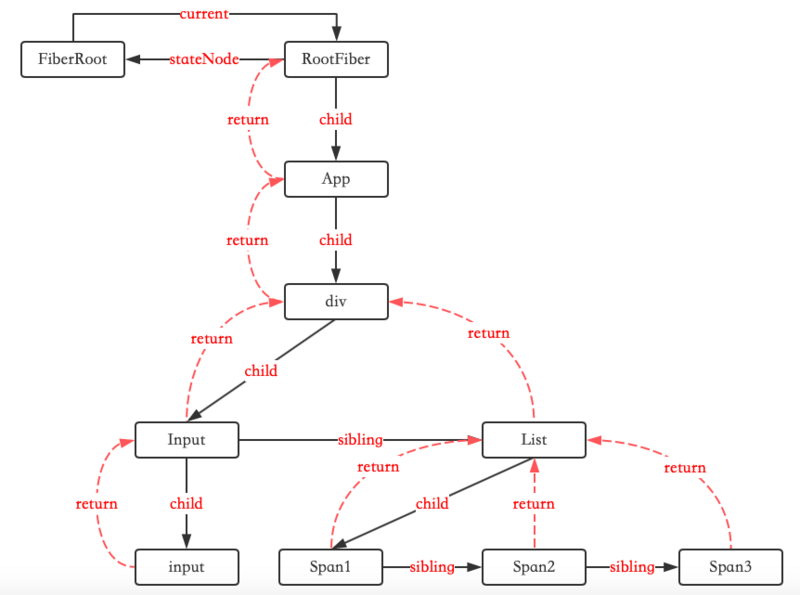
我们从这张图可以看出:
- FiberRoot 和 RootFiber 的双向链接关系。
- Fiber 中 child 为子节点指针,sibling 为兄弟节点指针,return 为父节点指针,这三个指针共同构成了 FiberTree 的数据结构。注意 sibling 只指向下一个兄弟节点。
- 从整体上看,child 指针和 return 指针决定了深度关系,而 sibling 指针决定了广度关系。return 指针决定了 FiberTree 的可逆性。
Local Stack
到目前为止,我们来看一下目前的调用栈:
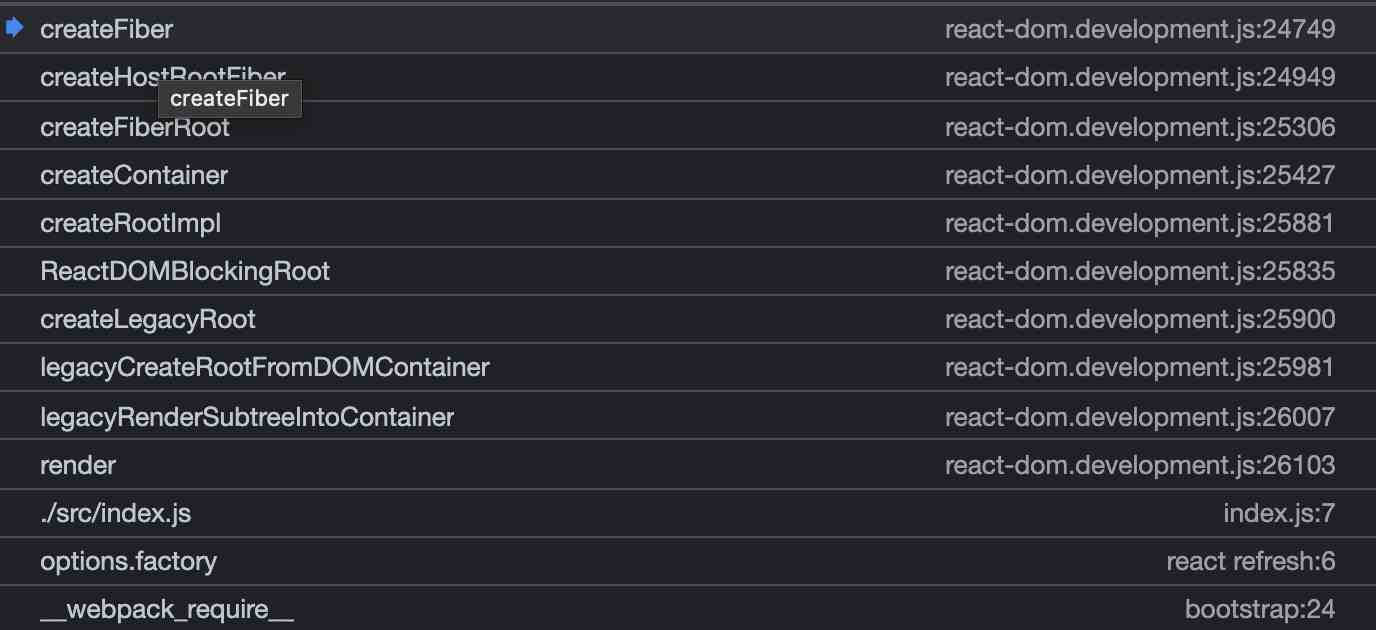
过程如下: render -> legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer -> legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer -> createContainer -> createFiberRoot -> createHostRootFiber -> createFiber -> ...
# flushSync
从上面的过程,已经创建了 HostRoot 和 RootFiber,以及
flushSync(() => {
updateContainer(children, fiberRoot, parentComponent, callback);
});
2
3
flushSync 函数处理同步渲染,在传入的回调中调用了 updateContainer 函数。
下面是 flushSync 函数:
// Overload the definition to the two valid signatures.
// Warning, this opts-out of checking the function body.
declare function flushSync<R>(fn: () => R): R;
// eslint-disable-next-line no-redeclare
declare function flushSync(): void;
// eslint-disable-next-line no-redeclare
export function flushSync(fn) {
// In legacy mode, we flush pending passive effects at the beginning of the
// next event, not at the end of the previous one.
// rootWithPendingPassiveEffects 表示当前已经 commit 的 HostRoot
// 如果当前已存在 commit 的 HostRoot,且当前执行阶段不是 RenderContext 或者 CommitContext,则 flush 所有待渲染的副作用
if (
rootWithPendingPassiveEffects !== null &&
rootWithPendingPassiveEffects.tag === LegacyRoot &&
(executionContext & (RenderContext | CommitContext)) === NoContext
) {
flushPassiveEffects();
}
const prevExecutionContext = executionContext;
// executionContext 指向 BatchedContext
executionContext |= BatchedContext;
const prevTransition = ReactCurrentBatchConfig.transition;
const previousPriority = getCurrentUpdatePriority();
try {
ReactCurrentBatchConfig.transition = 0;
setCurrentUpdatePriority(DiscreteEventPriority);
if (fn) {
return fn();
} else {
return undefined;
}
} finally {
// 如果 fn 执行 抛出了错误,则回退至之前的状态
setCurrentUpdatePriority(previousPriority);
ReactCurrentBatchConfig.transition = prevTransition;
executionContext = prevExecutionContext;
// Flush the immediate callbacks that were scheduled during this batch.
// Note that this will happen even if batchedUpdates is higher up
// the stack.
// flush 本次 batch 中高优先级的 callbacks
if ((executionContext & (RenderContext | CommitContext)) === NoContext) {
flushSyncCallbacks();
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
- flushSync 使用了 ts 的函数重载,如果传入回调,会执行这个回调。
- 从整体来看,flushSync 主要调用了 flushPassiveEffects 函数来处理已经 commit 的 HostRoot 上的待执行的副作用。
- flushSync 会先对已经 commit 的内容执行 flushPassiveEffects,执行完毕后才进入 BatchedContext 阶段。
- 注意,在首次渲染时 rootWithPendingPassiveEffects 应该为 null,也就是说 flushPassiveEffects 不会被执行到,但是我们仍然来分析下 flushPassiveEffects 会做些什么事情。
# flushPassiveEffects
// src/react/packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberWorkLoop.new.js
export function flushPassiveEffects(): boolean {
// Returns whether passive effects were flushed.
// TODO: Combine this check with the one in flushPassiveEFfectsImpl. We should
// probably just combine the two functions. I believe they were only separate
// in the first place because we used to wrap it with
// `Scheduler.runWithPriority`, which accepts a function. But now we track the
// priority within React itself, so we can mutate the variable directly.
if (rootWithPendingPassiveEffects !== null) {
// Cache the root since rootWithPendingPassiveEffects is cleared in
// flushPassiveEffectsImpl
// 这里缓存 root 是为了在发生错误回滚时即时释放缓存池
const root = rootWithPendingPassiveEffects;
// Cache and clear the remaining lanes flag; it must be reset since this
// method can be called from various places, not always from commitRoot
// where the remaining lanes are known
// 重置 remainingLanes
const remainingLanes = pendingPassiveEffectsRemainingLanes;
pendingPassiveEffectsRemainingLanes = NoLanes;
const renderPriority = lanesToEventPriority(pendingPassiveEffectsLanes);
const priority = lowerEventPriority(DefaultEventPriority, renderPriority);
const prevTransition = ReactCurrentBatchConfig.transition;
const previousPriority = getCurrentUpdatePriority();
try {
ReactCurrentBatchConfig.transition = 0;
setCurrentUpdatePriority(priority);
return flushPassiveEffectsImpl();
} finally {
// flushPassiveEffectsImpl 发生错误后回滚只上一状态
setCurrentUpdatePriority(previousPriority);
ReactCurrentBatchConfig.transition = prevTransition;
// Once passive effects have run for the tree - giving components a
// chance to retain cache instances they use - release the pooled
// cache at the root (if there is one)
releaseRootPooledCache(root, remainingLanes);
}
}
return false;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
这个函数主要调用 flushPassiveEffectsImpl 函数。
function flushPassiveEffectsImpl() {
if (rootWithPendingPassiveEffects === null) {
return false;
}
const root = rootWithPendingPassiveEffects;
const lanes = pendingPassiveEffectsLanes;
// 由于这里的 PassiveEffects 将会被 flush,这里将之清空
rootWithPendingPassiveEffects = null;
// TODO: This is sometimes out of sync with rootWithPendingPassiveEffects.
// Figure out why and fix it. It's not causing any known issues (probably
// because it's only used for profiling), but it's a refactor hazard.
pendingPassiveEffectsLanes = NoLanes;
// Render 阶段和 Commit 阶段是不能 flush 的
if ((executionContext & (RenderContext | CommitContext)) !== NoContext) {
throw new Error('Cannot flush passive effects while already rendering.');
}
const prevExecutionContext = executionContext;
// 将 executionContext 更新为 CommitContext,因为现在进入了 Commit 阶段
executionContext |= CommitContext;
// 这里将 passiveEffects 分成了 Mount 和 Unmount 阶段,这两类都需要 commit,但是处理的逻辑不同
commitPassiveUnmountEffects(root.current);
commitPassiveMountEffects(root, root.current);
executionContext = prevExecutionContext;
// 所有的同步的 callback 都需要 flush
flushSyncCallbacks();
// If additional passive effects were scheduled, increment a counter. If this
// exceeds the limit, we'll fire a warning.
// nestedPassiveUpdateCount 计数器递增,防止造成死循环
nestedPassiveUpdateCount =
rootWithPendingPassiveEffects === null ? 0 : nestedPassiveUpdateCount + 1;
return true;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
- flush effects 的目的是 commit effects。
# flushSyncCallbacks
// src/react/packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberSyncTaskQueue.new.js
export function flushSyncCallbacks() {
// isFlushingSyncQueue 是 syncQueue 的互斥锁
if (!isFlushingSyncQueue && syncQueue !== null) {
// Prevent re-entrance.
isFlushingSyncQueue = true;
let i = 0;
const previousUpdatePriority = getCurrentUpdatePriority();
try {
const isSync = true;
const queue = syncQueue;
// TODO: Is this necessary anymore? The only user code that runs in this
// queue is in the render or commit phases.
setCurrentUpdatePriority(DiscreteEventPriority);
// flush syncQueue,每个 callback 可以返回一个新的 callback
for (; i < queue.length; i++) {
let callback = queue[i];
do {
callback = callback(isSync);
} while (callback !== null);
}
// 重置 syncQueue
syncQueue = null;
includesLegacySyncCallbacks = false;
} catch (error) {
// If something throws, leave the remaining callbacks on the queue.
// 如果syncQueue 中每个 RootCallback 发生了错误,则跳过此项
if (syncQueue !== null) {
syncQueue = syncQueue.slice(i + 1);
}
// Resume flushing in the next tick
// 调度在下一个 tick 中继续执行
scheduleCallback(ImmediatePriority, flushSyncCallbacks);
throw error;
} finally {
setCurrentUpdatePriority(previousUpdatePriority);
isFlushingSyncQueue = false;
}
}
return null;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
可以看到,flushSyncCallbacks 主要是在执行完 syncQueue 中的所有的回调,syncQueue 中的 callback 可以返回一个新的 callback,这种结构类似于数组 + 链表和结构,很是巧妙。这段代码中 syncQueue 的数据结构、flush syncQueue 的处理方式和错误处理方式,值得我们借鉴。这种消费 effect 的方式和 react 中响应式 effect 的消费很像。
- 因为 syncQueue 是公共资源,而 flushSyncCallbacks 是其消费者,因此消费者在消费 syncQueue 时需要添加互斥锁,以免造成资源争夺。
- 出现错误时并不是直接继续执行,而是放到了 next tick 中继续消费,提高了 syncQueue 消费的效率。
# updateContainer
updateContainer 是首次渲染中重要工作中的一项。
export function updateContainer(
element: ReactNodeList,
container: OpaqueRoot,
parentComponent: ?React$Component<any, any>,
callback: ?Function,
): Lane {
// 获取 RootFiber
const current = container.current;
const eventTime = requestEventTime();
const lane = requestUpdateLane(current);
// 更新 container 的 context 信息
const context = getContextForSubtree(parentComponent);
if (container.context === null) {
container.context = context;
} else {
container.pendingContext = context;
}
// 创建一个更新
const update = createUpdate(eventTime, lane);
// Caution: React DevTools currently depends on this property
// being called "element".
update.payload = {element};
callback = callback === undefined ? null : callback;
if (callback !== null) {
update.callback = callback;
}
// 将新建的更新入栈
enqueueUpdate(current, update, lane);
// 请求一次调度更新
const root = scheduleUpdateOnFiber(current, lane, eventTime);
if (root !== null) {
entangleTransitions(root, current, lane);
}
return lane;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
updateContainer 函数中主要是针对 RootFiber 创建了一次更新,加入到更新队列,并且请求调度器进行调度。调度更新部分,请参照 scheduleWork 与调度过程 。
# 小结
通过上面的分析过程可知,React 的首次渲染的流程如下:首先执行一系列的初始化工作,包括创建 HostRoot 和 FiberRoot 以及建立两者之间的关联、初始化事件委托系统,然后创建一个同步的更新并向调度器提交调度请求。
# Q&A
# executionContext 有哪几种?
executionContext 表示 React 当前执行的上下文阶段,通过 executionContext 我们可以大致分出其总体渲染流程的不同阶段。
// src/react/packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberWorkLoop.new.js
export const NoContext = /* */ 0b0000;
const BatchedContext = /* */ 0b0001; // Batch(批处理)阶段
const RenderContext = /* */ 0b0010; // Render(渲染)阶段
const CommitContext = /* */ 0b0100; // Commit(提交)阶段
export const RetryAfterError = /* */ 0b1000; // 错误重试阶段
// Describes where we are in the React execution stack
let executionContext: ExecutionContext = NoContext;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
全局变量 executionContext 代表当前的执行上下文,初始化为 NoContent。下面是这四个阶段的对照表格:
| context | 所在函数 | 阶段 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|
| NoContext | 初始化 | 初始阶段 | |
| BatchedContext | flushSync、batchedUpdates、flushControlled | Batch (批处理) 阶段 | RenderSubtreeIntoContainer 之后,renderRoot 之前 |
| RenderContext | renderRootSync、renderRootConcurrent | Render (渲染) 阶段 | renderRoot 之后,commitRoot 之前 |
| CommitContext | commitRootImpl、flushPassiveEffectsImpl | Commit (提交) 阶段 | commitRoot 之后 |
| RetryAfterError | recoverFromConcurrentError | Error 阶段 | 发生错误需要恢复之后 |
从表格可以总结出,React 的渲染总共分为 NoContext、BatchedContext、RenderContext、CommitContext、RetryAfterError 五个阶段。关于更新阶段的更多内容,请移步 React 更新周期。
# 使用位运算提高枚举计算效率
React 中多处使用位运算进行枚举计算,使用位运算可以有效提交运行效率,尤其是大型的状态繁多的项目。在 react 源码中有很多类似的位运算,比如 effectTag,workTag 和上文中的 executionContext。
下面我们来看看 React 中位运算枚举风格:
const NoContext = 0b0000;
const BatchedContext = 0b0001;
const RenderContext = 0b0010;
const CommitContext = 0b0100;
const RetryAfterError = 0b1000;
let executionContext = NoContext;
// 如果现在开始 RenderContainer,进入 Batch 阶段
// 增加枚举值
executionContext |= BatchedContext; // 1
// 判断是否在 Batch 阶段
// 消费枚举值:0 表示没有枚举值,1 表示有枚举值。这里我们直接跟为 0 的 NoContext 作比较。
(executionContext & BatchedContext) !== NoContext; // true
// 判断是否处于 Render 阶段
(executionContext & RenderContext) !== NoContext; // false
// 现在开始 RenderRoot,进入 Render 阶段
executionContext |= RenderContext;
// 判断是否处于 Batch 阶段或者 Render 阶段
(executionContext & (BatchedContext | RenderContext)) !== NoContext; // true
// 判断是否不处于 Commit 阶段或者 Error 阶段
(executionContext & (CommitContext | RetryAfterError)) === NoContext; // true
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
下面我们再来对比一些 Vue 源码中使用位运算的风格。
const enum ShapeFlags {
ELEMENT = 1,
FUNCTIONAL_COMPONENT = 1 << 1,
STATEFUL_COMPONENT = 1 << 2,
TEXT_CHILDREN = 1 << 3,
ARRAY_CHILDREN = 1 << 4,
SLOTS_CHILDREN = 1 << 5,
TELEPORT = 1 << 6,
SUSPENSE = 1 << 7,
COMPONENT_SHOULD_KEEP_ALIVE = 1 << 8,
COMPONENT_KEPT_ALIVE = 1 << 9,
COMPONENT = ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT | ShapeFlags.FUNCTIONAL_COMPONENT
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
写法不一样,使用的方法是一样的。
这种原理是什么?这是因为这些枚举数字是互相正交的(可以从数学上垂直的概念来理解),也可以从二进制为进行理解,没加入一个枚举值,在相应的下标出置为 1(按位或运算),判断是否有这个枚举值的时候,就可以那要判断的值与枚举值对齐比对(按位与运算)。
位运算的更多技巧请参考文章:位运算初探
