 ReactDOM.render 方法
ReactDOM.render 方法
# 目录
# ReactDOM 是什么?
在 react-dom 包中 ReactDOM.js 里定义了 ReactDOM。大致如下:
const ReactDOM: Object = {
createPortal, // 创建 portal
findDOMNode, // 获取 DOM
hydrate,
render,
unstable_renderSubtreeIntoContainer,
unmountComponentAtNode,
unstable_batchedUpdates,
unstable_interactiveUpdates,
unstable_discreteUpdates,
unstable_flushDiscreteUpdates,
flushSync,
unstable_createRoot,
unstable_createSyncRoot,
unstable_flushControlled,
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# render 方法
render 方法:
render(
element: React$Element < any >, // render 的元素
container: DOMContainer, // render 的容器
callback: ?Function, // callback
) {
return legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer(
null,
element,
container,
false,
callback,
);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
在 root 刚刚被创建时, parentComponent 一般都为 null;
内部调用 legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer 方法,代码如下:
function legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer(
parentComponent: ? React$Component < any, any > ,
children : ReactNodeList, // 待渲染的元素
container: DOMContainer, // 渲染的目标容器
forceHydrate: boolean,
callback: ? Function,
) {
let root: _ReactSyncRoot = (container._reactRootContainer: any);
let fiberRoot;
if (!root) {
// Initial mount
// 获取到 ReactSyncRoot 实例
root = container._reactRootContainer = legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer(
container,
forceHydrate,
);
console.log('==>legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer_获取到 ReactSyncRoot 实例', {
root
});
// {
// _internalRoot: FiberRootNode // 内部的 fiber 节点
// callbackExpirationTime: 0
// callbackNode: null
// callbackPriority: 90
// containerInfo: div#root // ROOT 的 DOM 节点
// context: {}
// current: FiberNode {tag: 3, key: null, elementType: null, type: null, stateNode: FiberRootNode, …}
// finishedExpirationTime: 0
// finishedWork: null
// firstBatch: null
// firstPendingTime: 0
// firstSuspendedTime: 0
// hydrate: false
// interactionThreadID: 1
// lastExpiredTime: 0
// lastPingedTime: 0
// lastSuspendedTime: 0
// memoizedInteractions: Set(0) {}
// nextKnownPendingLevel: 0
// pendingChildren: null
// pendingContext: null
// pendingInteractionMap: Map(0) {}
// pingCache: null
// tag: 0
// timeoutHandle: -1
// }
fiberRoot = root._internalRoot;
if (typeof callback === 'function') {
const originalCallback = callback;
callback = function () {
// 通过 public 的 root 实例去调用 callback
const instance = getPublicRootInstance(fiberRoot);
console.log('==>getPublicRootInstance_可被 callback 的 root 实例', {
instance
});
// instance: null
originalCallback.call(instance);
};
}
// Initial mount should not be batched.
// render 为首次渲染,则不需要 batchedUpdates
unbatchedUpdates(() => {
// 响应更新
updateContainer(children, fiberRoot, parentComponent, callback);
});
} else {
// 如果 root 已经存在,则直接响应更新
fiberRoot = root._internalRoot;
if (typeof callback === 'function') {
const originalCallback = callback;
callback = function () {
const instance = getPublicRootInstance(fiberRoot);
originalCallback.call(instance);
};
}
// Update
updateContainer(children, fiberRoot, parentComponent, callback);
}
// 返回 public 的 root 实例
// render 函数是有返回值的,返回一个根节点的实例。
return getPublicRootInstance(fiberRoot);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
- 当 render () 被调用时,
legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer这个函数首先会去获取一个_ReactSyncRoot的实例,称之为 root,而真正需要更新使用的fiberRoot = root._internalRoot。 - render () 函数中传入的 callback 函数会被包装, 通过 public 的 root 实例去调用 callback。
- render 函数的更新是不需要 patch 的,因为它是根组件挂载时的首次更新,它会相应的调用
unbatchedUpdates()来触发更新。 - 无论是否需要 patch 的更新,都需要调用
updateContainer进行更新操作。
# 创建 ReactRoot
root = container._reactRootContainer = legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer(
container,
forceHydrate,
);
2
3
4
通过 legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer 方法创建 ReactRoot ,ReatRoot 实际上是一个 ReactSyncRoot 的实例,这个实例被挂载到 container._reactRootContainer 上。
legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer 方法如下:
function legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer(
container: DOMContainer,
forceHydrate: boolean,
): _ReactSyncRoot {
// 是否应该 Hydrate
const shouldHydrate =
forceHydrate || shouldHydrateDueToLegacyHeuristic(container);
// First clear any existing content.
if (!shouldHydrate) {
let rootSibling;
// lastChild 属性返回被选节点的最后一个子节点。如果选定的节点没有子节点,则该属性返回 NULL。
// 循环删除尾结点,实际上是清空容器
while ((rootSibling = container.lastChild)) {
container.removeChild(rootSibling);
}
}
// Legacy roots are not batched.
return new ReactSyncRoot(
container,
LegacyRoot, // root 标记
shouldHydrate ?
{
hydrate: true,
} :
undefined,
);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
- 为什么要清空容器?在将根组件渲染到 root 容器之前,应该保证容器为空。
- 什么是 hydrate? (opens new window)
- LegacyRoot 是一个常量,代表的是传统的同步的渲染方式。
# 一些数据结构
# FiberRoot
fiberRoot 的类型为 FiberRoot。fiberRoot 用于 react 的 updateContainer () 调用。
在 react-reconciler/ReactFiberRoot.js 中定义如下:
export type FiberRoot = {
...BaseFiberRootProperties,
...ProfilingOnlyFiberRootProperties,
...SuspenseCallbackOnlyFiberRootProperties,
};
2
3
4
5
重点来看 BaseFiberRootProperties 的类型:
type BaseFiberRootProperties = {
|
// The type of root (legacy, batched, concurrent, etc.)
// tag 类型
// export type RootTag = 0 | 1 | 2;
// export const LegacyRoot = 0;
// export const BatchedRoot = 1;
// export const ConcurrentRoot = 2;
tag: RootTag,
// Any additional information from the host associated with this root.
// 容器信息
containerInfo: any,
// Used only by persistent updates.
pendingChildren: any,
// The currently active root fiber. This is the mutable root of the tree.
// 当前容器的 Fiber 对象
current: Fiber,
pingCache:
|
WeakMap < Thenable,
Set < ExpirationTime >>
|
Map < Thenable,
Set < ExpirationTime >>
|
null,
finishedExpirationTime: ExpirationTime,
// A finished work-in-progress HostRoot that's ready to be committed.
// 将被 commit 的 Fiber
finishedWork: Fiber | null,
// Timeout handle returned by setTimeout. Used to cancel a pending timeout, if
// it's superseded by a new one.
timeoutHandle: TimeoutHandle | NoTimeout,
// Top context object, used by renderSubtreeIntoContainer
context: Object | null,
pendingContext: Object | null,
// Determines if we should attempt to hydrate on the initial mount
// 是否需要在初次渲染时进行hydrate
+hydrate: boolean,
// List of top-level batches. This list indicates whether a commit should be
// deferred. Also contains completion callbacks.
// TODO: Lift this into the renderer
firstBatch: Batch | null,
// Node returned by Scheduler.scheduleCallback
callbackNode: * ,
// Expiration of the callback associated with this root
// callback 的超时时间
callbackExpirationTime: ExpirationTime,
// Priority of the callback associated with this root
callbackPriority: ReactPriorityLevel,
// The earliest pending expiration time that exists in the tree
firstPendingTime: ExpirationTime,
// The earliest suspended expiration time that exists in the tree
firstSuspendedTime: ExpirationTime,
// The latest suspended expiration time that exists in the tree
lastSuspendedTime: ExpirationTime,
// The next known expiration time after the suspended range
nextKnownPendingLevel: ExpirationTime,
// The latest time at which a suspended component pinged the root to
// render again
lastPingedTime: ExpirationTime,
lastExpiredTime: ExpirationTime,
|
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
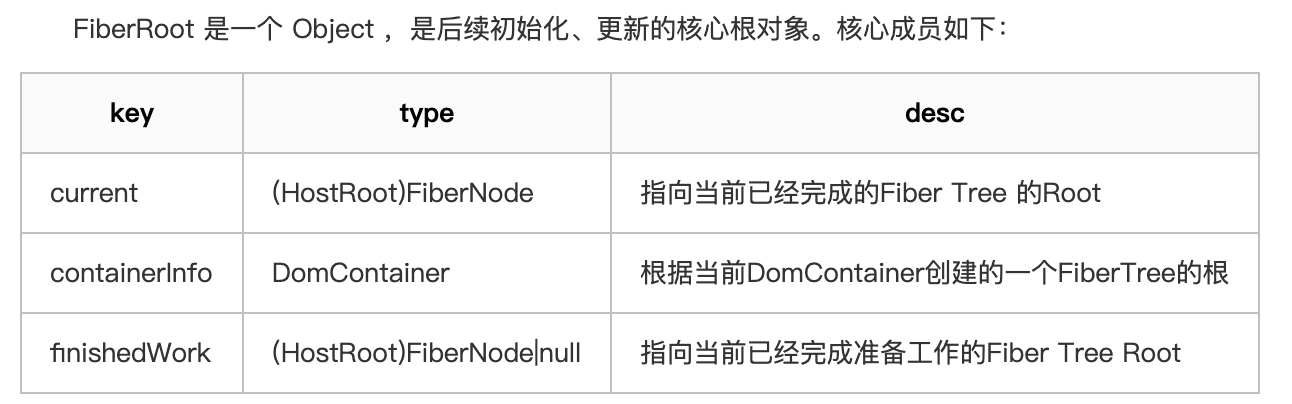
FiberRoot 数据结构归结如下:
# updateContainer () 方法
在 batchedUpdates() 和 unbatchedUpdates() 方法中会调用 updateContainer() 方法来更新视图。
updateContainer() 方法如下:
function updateContainer(
element: ReactNodeList,
container: OpaqueRoot,
parentComponent: ? React$Component < any, any > ,
callback : ? Function,
): ExpirationTime {
// 当前容器的 Fiber 对象
const current = container.current;
const currentTime = requestCurrentTime();
const suspenseConfig = requestCurrentSuspenseConfig();
const expirationTime = computeExpirationForFiber(
currentTime,
current,
suspenseConfig,
);
return updateContainerAtExpirationTime(
element,
container,
parentComponent,
expirationTime,
suspenseConfig,
callback,
);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
这个方法接受了 element、container、parentComponent 和 callback,返回一个 ExpirationTime 实例。它的只要作用是计算 expirationTime 和 suspenseConfig。
requestCurrentSuspenseConfig()方法返回ReactCurrentBatchConfig.suspense,即是当前 batch 的配置信息。
/**
* Keeps track of the current batch's configuration such as how long an update
* should suspend for if it needs to.
*/
// 当前 batch 的配置
const ReactCurrentBatchConfig = {
suspense: (null: null | SuspenseConfig),
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
- [[ExpirationTime,context 的计算方法]]
computeExpirationForFiber(
currentTime: ExpirationTime,
fiber: Fiber,
suspenseConfig: null | SuspenseConfig,
): ExpirationTime {
const mode = fiber.mode;
if ((mode & BatchedMode) === NoMode) {
console.log('==>', {mode, BatchedMode});
// {mode: 8, BatchedMode: 2}
// 8&2=0
return Sync; // 1073741823 MAX_SIGNED_31_BIT_INT
}
const priorityLevel = getCurrentPriorityLevel();
if ((mode & ConcurrentMode) === NoMode) {
console.log('==>', {mode, ConcurrentMode});
return priorityLevel === ImmediatePriority ? Sync : Batched;
}
if ((executionContext & RenderContext) !== NoContext) {
console.log('==>', {executionContext, RenderContext});
// Use whatever time we're already rendering
// TODO: Should there be a way to opt out, like with `runWithPriority`?
return renderExpirationTime; // NoWork 0
}
let expirationTime;
if (suspenseConfig !== null) {
// Compute an expiration time based on the Suspense timeout.
expirationTime = computeSuspenseExpiration(
currentTime,
suspenseConfig.timeoutMs | 0 || LOW_PRIORITY_EXPIRATION,
);
} else {
// Compute an expiration time based on the Scheduler priority.
switch (priorityLevel) {
case ImmediatePriority:
expirationTime = Sync;
break;
case UserBlockingPriority:
// TODO: Rename this to computeUserBlockingExpiration
expirationTime = computeInteractiveExpiration(currentTime);
break;
case NormalPriority:
case LowPriority: // TODO: Handle LowPriority
// TODO: Rename this to... something better.
expirationTime = computeAsyncExpiration(currentTime);
break;
case IdlePriority:
expirationTime = Idle;
break;
default:
invariant(false, 'Expected a valid priority level');
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
下面就是 updateContainerAtExpirationTime() 方法。这里的主要作用就是计算 context。
function updateContainerAtExpirationTime(
element: ReactNodeList,
container: OpaqueRoot,
parentComponent: ? React$Component < any, any > ,
expirationTime : ExpirationTime,
suspenseConfig: null | SuspenseConfig,
callback: ? Function,
) {
const current = container.current;
// 通过子树计算context,挂载到 container.context 或者 container.pendingContext
const context = getContextForSubtree(parentComponent);
if (container.context === null) {
container.context = context;
} else {
container.pendingContext = context;
}
return scheduleRootUpdate(
current,
element,
expirationTime,
suspenseConfig,
callback,
);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
- [[ExpirationTime,context 的计算方法]]
继续调用 scheduleRootUpdate() 方法。这里是 render 的核心方法之一,只要是起到调度根节点更新的作用。在此函数里将创建更新、更新入队、调度更新。
function scheduleRootUpdate(
current: Fiber,
element: ReactNodeList,
expirationTime: ExpirationTime,
suspenseConfig: null | SuspenseConfig,
callback: ? Function,
) {
// 根据当前render 的expirationTime和suspenseConfig 创建更新对象,称为一个 update。
const update = createUpdate(expirationTime, suspenseConfig);
callback = callback === undefined ? null : callback;
if (callback !== null) {
warningWithoutStack(
typeof callback === 'function',
'render(...): Expected the last optional `callback` argument to be a ' +
'function. Instead received: %s.',
callback,
);
// 将 callback 挂载到 update上
update.callback = callback;
}
// 更新入队列
enqueueUpdate(current, update);
// 在expirationTime时调度更新
scheduleWork(current, expirationTime);
return expirationTime;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
下面重点来追溯 createUpdate() 、 enqueueUpdate() 和 scheduleWork() 方法。
# createUpdate () 创建更新
创建一个 Update 对象。其中 tag 为 UpdateState 表示更新状态。
// 函数createUpdate会创建一个update对象,用于存放更新的状态partialState、状态更新后的回调函数callback和渲染的过期时间expirationTime。
function createUpdate(
expirationTime: ExpirationTime,
suspenseConfig: null | SuspenseConfig,
): Update < * > {
let update: Update < * > = { // 初始化update对象的属性
expirationTime, // 过时时间
suspenseConfig, // 暂停配置
tag: UpdateState, // 常量标签,0,UpdateState表示这是一个更新状态的操作,值为0
payload: null, // 负载更新内容,比如`setState`接收的第一个参数
callback: null, // 回调函数
next: null, // 队列下一项更新的指针
nextEffect: null, // 指向下一项副作用更新的指针
};
if (__DEV__) {
update.priority = getCurrentPriorityLevel();
}
return update;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
Update 的类型如下:
type Update < State > = {
expirationTime: ExpirationTime,
suspenseConfig: null | SuspenseConfig,
tag: 0 | 1 | 2 | 3,
payload: any,
callback: (() => mixed) | null,
next: Update < State > | null,
nextEffect: Update < State > | null,
//DEV only
priority ? : ReactPriorityLevel,
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
- next 和 nextEffect 都是指向更新的指针。
- Update 的 tag 类型如下:
export const UpdateState = 0;
export const ReplaceState = 1;
export const ForceUpdate = 2;
export const CaptureUpdate = 3;
2
3
4
Update 的数据结构归结如下:
| key | type | desc |
|---|---|---|
| tag | Number | 当前有 0~3,分别是 UpdateState、ReplaceState、ForceUpdate、CaptureUpdate |
| payload | Function|Object | 表示这个更新对应的数据内容 |
| callback | Function | 表示更新后的回调函数,如果这个回调有值,就会在 UpdateQueue 的副作用链表中挂载当前 Update 对象 |
| next | Update | UpdateQueue 中的 Update 之间通过 next 来串联,表示下一个 Update 对象 |
# enqueueUpdate () 更新入队
创建 update 之后,需要将此 update 放入队列。 enqueueUpdate() 函数传入 fiber 和 update 两个参数。在看这里代码之前,先看看 fider 和 update 是什么样子的。
fiber:
{
actualDuration: 0
actualStartTime: -1
alternate: FiberNode { // alternate也是一个FiberNode
tag: 3,
key: null,
elementType: null,
type: null,
stateNode: FiberRootNode,
…
}
child: null
childExpirationTime: 0
dependencies: null
effectTag: 0
elementType: null
expirationTime: 1073741823
firstEffect: null
index: 0
key: null
lastEffect: null
memoizedProps: null
memoizedState: null
mode: 8
nextEffect: null
pendingProps: null
ref: null
return :null
selfBaseDuration: 0
sibling: null
stateNode: FiberRootNode {
tag: 0,
current: FiberNode,
containerInfo: div# root,
pendingChildren: null,
pingCache: null,
…
}
tag: 3
treeBaseDuration: 0
type: null
updateQueue: {
baseState: null,
firstUpdate: {
…},
lastUpdate: {
…},
firstCapturedUpdate: null,
lastCapturedUpdate: null,
…
}
_debugHookTypes: null
_debugID: 1
_debugIsCurrentlyTiming: false
_debugNeedsRemount: false
_debugOwner: null
_debugSource: null
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
update:
{
callback: null
expirationTime: 1073741823
next: null
nextEffect: null
payload: {
element: {$$typeof: Symbol(react.element), key: null, ref: null, props: {…}, type: ƒ, …}
}
priority: 97
suspenseConfig: null
tag: 0
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
下面再来看看 enqueueUpdate() 方法:
/**
* @desc enqueueUpdate将update对象加入到队列,创建队列或者将更新加入队列尾部
* @param 接受Fiber和update对象,Fiber本意为纤维
* @returns
*/
function enqueueUpdate < State > (fiber: Fiber, update: Update < State > ) {
// Update queues are created lazily.
const alternate = fiber.alternate; // workInProgress fiber
// 两个队列分别为 current fiber 和 workInProgress fiber 的队列。
let queue1;
let queue2;
if (alternate === null) { // 首次渲染
// There's only one fiber.
queue1 = fiber.updateQueue;
queue2 = null;
if (queue1 === null) { // 当前没有队列
// 创建更新队列, fiber.memoizedState是baseState
queue1 = fiber.updateQueue = createUpdateQueue(fiber.memoizedState);
}
} else {
// There are two owners.alternate不为null,workInProgress fiber 存在
queue1 = fiber.updateQueue;
queue2 = alternate.updateQueue;
if (queue1 === null) {
if (queue2 === null) {
// Neither fiber has an update queue. Create new ones.
queue1 = fiber.updateQueue = createUpdateQueue(fiber.memoizedState);
queue2 = alternate.updateQueue = createUpdateQueue(
alternate.memoizedState,
);
} else {
// Only one fiber has an update queue. Clone to create a new one.
queue1 = fiber.updateQueue = cloneUpdateQueue(queue2);
}
} else {
if (queue2 === null) {
// Only one fiber has an update queue. Clone to create a new one.
queue2 = alternate.updateQueue = cloneUpdateQueue(queue1);
} else {
// Both owners have an update queue.
}
}
}
if (queue2 === null || queue1 === queue2) { // 只有一个队列,将更新加入到队列
// There's only a single queue.
appendUpdateToQueue(queue1, update);
} else {
// There are two queues. We need to append the update to both queues,
// while accounting for the persistent structure of the list — we don't
// want the same update to be added multiple times.
if (queue1.lastUpdate === null || queue2.lastUpdate === null) { // 将更新加入到两个队列
// One of the queues is not empty. We must add the update to both queues.
appendUpdateToQueue(queue1, update);
appendUpdateToQueue(queue2, update);
} else {
// Both queues are non-empty. The last update is the same in both lists,
// because of structural sharing. So, only append to one of the lists.
appendUpdateToQueue(queue1, update);
// But we still need to update the `lastUpdate` pointer of queue2.
queue2.lastUpdate = update;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
- fiber.aternate 是什么? 在任何时候,一个组件实例最多有两个与之对应的 Fiber 对象:当前即将渲染的(current fiber)和 workInProgress fiber,diff 产生出的变化会标记在 workInProgress fiber 上。current fiber 的 alternate 是 workInProgress fiber,workInProgress fiber 的 alternate 是 current fiber。workInProgress 构造完毕,得到了新的 fiber,然后把 current 指针指向 workInProgress,丢掉旧的 fiber。Fiber 的 alternate 是一个叫 cloneFiber 的函数惰性的创建的,与总是创建一个新对象不同,cloneFiber 将尝试重用 Fiber 的 alternate(如果存在的话),以实现最小化内存分配。
参看:fiber.alternate (opens new window)
下面的就是几个队列的操作,在此之前先来看看队列是什么样子的。
{
queue1: {
baseState: null
firstCapturedEffect: null
firstCapturedUpdate: null
firstEffect: null
firstUpdate: {
expirationTime: 1073741823,
suspenseConfig: null,
tag: 0,
payload: {
…},
callback: null,
…
}
lastCapturedEffect: null
lastCapturedUpdate: null
lastEffect: null
lastUpdate: {
expirationTime: 1073741823,
suspenseConfig: null,
tag: 0,
payload: {
…},
callback: null,
…
}
__proto__: Object
},
queue2: null
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
- createUpdateQueue (fiber.memoizedState) 创建更新队列
fiber.memoizedState 在创建更新队列时会作为 baseState 传入。baseState 表示更新前的基础状态。初次渲染时 memoizedState 一般为 null。
/**
* @desc 创建空的UpdateQueue对象
* @param baseState: State
* @returns UpdateQueue<State>
*/
function createUpdateQueue < State > (baseState: State): UpdateQueue < State > {
const queue: UpdateQueue < State > = {
baseState,
firstUpdate: null, // 初次更新
lastUpdate: null, // 上次更新
firstCapturedUpdate: null, // 初次捕获更新
lastCapturedUpdate: null, // 最新捕获更新
firstEffect: null,
lastEffect: null,
firstCapturedEffect: null,
lastCapturedEffect: null,
};
return queue;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
UpdateQueue 的结构总结如下: 在 FiberNode 节点中表示当前节点更新、更新的副作用(主要是 Callback)的集合,下面的结构省略了 CapturedUpdate 部分。
| key | type | desc |
|---|---|---|
| baseState | Object | 表示更新前的基础状态 |
| firstUpdate | Update | 第一个 Update 对象引用,总体是一条单链表 |
| lastUpdate | Update | 最后一个 Update 对象引用 |
| firstEffect | Update | 第一个包含副作用(Callback)的 Update 对象的引用 |
| lastEffect | Update | 最后一个包含副作用(Callback)的 Update 对象的引用 |
- cloneUpdateQueue (queue) 复制队列
cloneUpdateQueue22 只会复制目标队列的 baseState、firstUpdate 和 lastUpdate 属性。
function cloneUpdateQueue < State > (
currentQueue: UpdateQueue < State > ,
): UpdateQueue < State > {
const queue: UpdateQueue < State > = {
baseState: currentQueue.baseState,
firstUpdate: currentQueue.firstUpdate,
lastUpdate: currentQueue.lastUpdate,
// TODO: With resuming, if we bail out and resuse the child tree, we should
// keep these effects.
firstCapturedUpdate: null,
lastCapturedUpdate: null,
firstEffect: null,
lastEffect: null,
firstCapturedEffect: null,
lastCapturedEffect: null,
};
return queue;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
- appendUpdateToQueue (queue, update) 添加更新到队列
appendUpdateToQueue () 中 firstUpdate 的更新会先执行,lastUpdate 会指向下一个更新,如果尾指针 lastUpdate 为 null,就需要把头指针和尾指针都指向 update,否则就把尾指针和尾指针的 next 指向 update。
/**
* @description 将更新加入到队列(尾部)
* @param {*} queue 队列
* @param {*} update 更新
*/
function appendUpdateToQueue < State > (
queue: UpdateQueue < State > ,
update: Update < State > ,
) {
// Append the update to the end of the list.
if (queue.lastUpdate === null) {
// Queue is empty // 空队列
queue.firstUpdate = queue.lastUpdate = update; // 头指针和尾指针都指向了update
} else {
queue.lastUpdate.next = update; // 将update挂载到尾指针的 next
queue.lastUpdate = update; // 将尾指针移动到 update
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
- queue 是怎么使用的?
queue1 被挂载在 fiber.updateQueue 上,queue2 被挂载在 fiber.alternate.updateQueue 上。updateQueue 是在 fiber 系统的基础上进行管理的。
queue1 = fiber.updateQueue = createUpdateQueue(fiber.memoizedState);
queue2 = alternate.updateQueue = createUpdateQueue(
alternate.memoizedState,
);
2
3
4
